
Electrical Basics: Part 2
Now that you know the difference between AC and DC Current, let’s dive into understanding the varying levels of VAC power that are typically involved with EV charging.

120 VAC
A low voltage that is commonly used in residential and commercial settings. It is used to power small appliances and electronics such as lamps, computers, and televisions.

240 VAC
Widely utilized in residential and commercial settings, 240V is suitable for larger appliances such as ovens and dryers. It often involves two 120V legs that are out of phase with each other, providing a higher voltage for increased power needs.

480 VAC
Common in industrial settings, especially with three-phase power systems, 480V is the voltage between phases in a 3-phase circuit. This level of power is associated with heavy machinery and industrial equipment.
HOW DOES THIS APPLY TO EV CHARGING?
For EV charging, any of these VAC levels may be employed depending on the application. Slower home chargers require 120 VAC that can be achieved simply by plugging the charging device into a common outlet. For high powered fast chargers, 480 VAC is required to achieve the massive power requirements. Those same chargers may also require 120 VAC to power the smaller electrical components on the chargers such as touchscreens, payment systems, and communication devices.
THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN SINGLE-PHASE POWER AND THREE-PHASE POWER
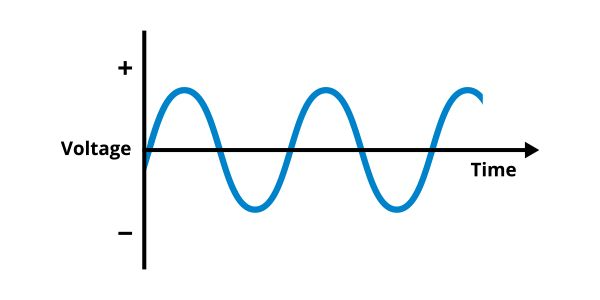
SINGLE-PHASE POWER
Single-phase power is a two-wire AC power circuit. It has one power wire, called the phase wire, and one neutral wire. The current flows between the power wire (through the load) and the neutral wire. Single-phase power is commonly used in residential homes for lighting or heating.
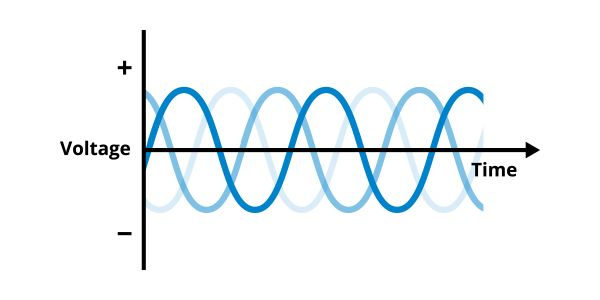
THREE-PHASE POWER
Three-phase power is a three-wire AC power circuit with each phase AC signal 120 degrees phase shifted relative to each wire. It is more commonly used in commercial and industrial facilities for delivering high power to heavy loads. Three-phase power systems are more efficient than single-phase power systems. A three-phase power system can transmit up to three times as much power as a single-phase power system, while only needing one additional wire (that is, three wires instead of two).
HOW DOES THIS APPLY TO EV CHARGING?
Because it can be used to deliver consistent and greater amounts of power, three-phase power is used in faster EV charging applications to provide high power transfer (>50kW) and faster recharge times - minutes instead of hours.
CLICK HERE to see Part 3 of the series, which takes a closer look at a vital component of EV Charging – Circuit Breakers.
